NumPy Benchmarks
Overview
This web page aims to benchmark NumPy’s performance on the widely accepted N-body problem [2]. This work also compares NumPy with Python & C++ and with compilers like Numba and Pythran.
The objective of benchmarking NumPy revolves around the efficiency of the library in quasi real-life situations, and the N-body problem suits the purpose well. Benchmarking is performed over several iterations for different datasets to ensure the accuracy of the results.
About N-Body Problem
In physics, the n-body problem is the problem of predicting the individual motions of a group of celestial objects interacting with each other gravitationally.
From the definition above, the N-body problem includes the kinematics between the different bodies, which involve various mathematical computations. Solving this problem has been motivated by the desire to understand the motions of the celestial bodies. Thus it serves as a robust entity between real-world applications and the computational world.
A brief description of computations involved in solving the N-body problem is given below, along with the pseudo-code in the next section:
Consider bodies of masses , moving under the mutual gravitational force of attraction between them in an inertial frame of reference of three dimensions, such that consecutive positions and velocities of an body are denoted by (, ) and (, ) respectively. According to the Newton’s law of gravity, the gravitational force felt on the body of mass by a single body of mass is denoted as and the acceleration of the body is represented as . Let and be the position vectors of two body, such that:
The final aim is to find time taken to evaluate the total energy of each particle in the celestial space at a given time step. The equations involved in solving the problem are listed below:
Pseudo Code of Solving N-body Problem
Set time to 0, time_step to 0.001 and time_end to 10s
THEN number_of_step is 10/0.001
FOR time is less than or equal to time_end
Calculate accelerations (a[i], for given position r[i])
Calculate total initial energies:
Calculate kinetic energy
Calculate potential energy
FOR k less than number_of_step
Calculate positions (r[k+1])
Swap accelerations
Calculate accelerations
Calculate velocities (v[k+1])
Increment time
IF number_of_step % 100 is not 0 THEN
Calculate total energy
Print energy
ENDIF
END FOR
END FOR
Dataset Description
- Nine different text files, named as
InputX.txt, where is number of particles in the celestial space (for this problem, number of particles are: and ). - Dataset[3] consists of the masses of each particle and information about their initial positions and velocities along the three-dimensional axis.
An example from the dataset[3] used is given below: (for a single particle, the values are approximated up to four decimal places for readability)
# Ordered as: label, mass (grams), position_x, position_y, position_z, velocity_x, velocity_y, velocity_z
-1 0.0625 0.2148 -0.1204 -0.2661 0.7578 0.1576 -0.0715
Compiled Methods
We considered accelerators like Numba, Pythran, and Transonic for benchmarking. This decision is inspired by Ralf Gommer’s Presentation on SciPy 1.0 (conference video). We give brief details on a few of the accelerators below:
Numba
Numba is an open source JIT compiler that translates a subset of Python and NumPy code into fast machine code.
Since Numba is a compiler focused on accelerating Python and NumPy codes,
the user API of the library supports various decorators.
It uses the industry-standard LLVM compiler library.
It aims to translate the Python functions to optimized machine code during runtime.
It supports variety of decorators like @jit, @vectorize, @guvectorize, @stencil, @jitclass, @cfunc, @overload.
We are using Just-In-Time compilation in this work.
It also supports nopython mode to generate fully compiled results
without the need for intermediate Python interpreter calls.
Numba’s assistance to NumPy arrays and functions also makes it a good candidate for comparison.
Pythran
Pythran is an ahead of time compiler for a subset of the Python language, with a focus on scientific computing.
Since the focus of Pythran was on accelerating Python and NumPy codes, its C++ API is the same as that of NumPy. Pythran also supports Expression Templating and SIMD instructions, which are its main advantages. It converts annotated Python modules into native Python modules, which are comparatively faster. But both have the same kind of interface.
Source Code
- The code is inspired by Pierre Augier’s work on N-Body Problem.
- Visualization Code: here.
| Algorithm & Source Code | Implementation Details |
| NumPy | Vectorized Approach, Broadcasting Method, NumPy Arrays |
| Python | Standard Python Approach, Using List |
| C++ | C++ Implementation, GNU C++ Compiler |
| Numba | Just-In-time Compilation, Non-Vectorized Approach, Using Numba at the Backend via Transonic, NumPy Arrays |
| Pythran | Just-In-Time Compilation, Non-Vectorized Approach, Pythran at the Backend via Transonic, NumPy Arrays |
Results
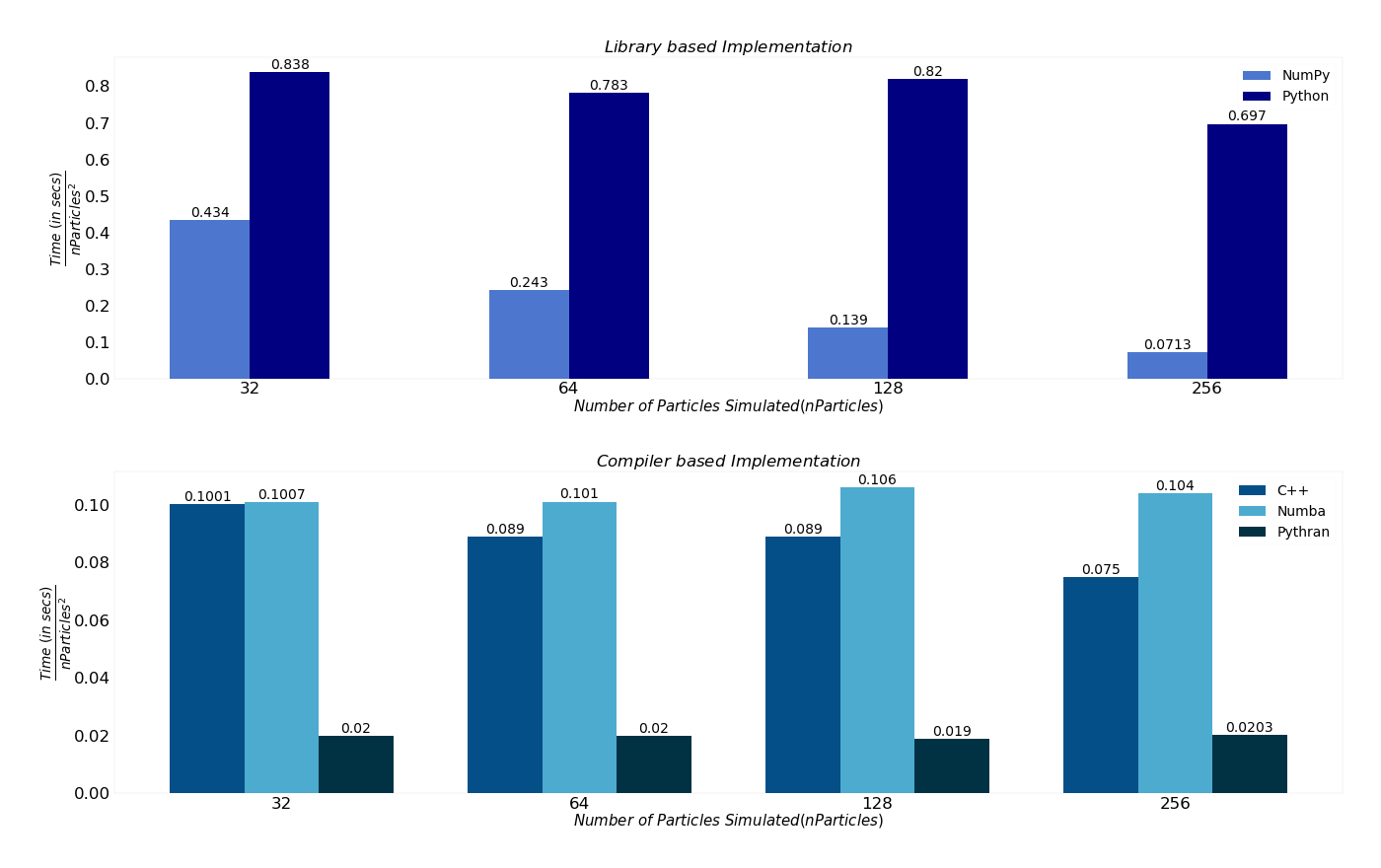
Table values represent the normalized time ‘time / nParticles^{2}` taken in seconds by each algorithm to run on the given datasets for number of iterations. The raw timing data can be downloaded from here.
| Input(s) | 32 | 64 | 128 | 256 |
| NumPy | 0.434 | 0.243 | 0.139 | 0.0713 |
| Python | 0.838 | 0.783 | 0.82 | 0.697 |
| C++ | 0.1001 | 0.089 | 0.089 | 0.075 |
| Numba | 0.1007 | 0.101 | 0.106 | 0.104 |
| Pythran | 0.02 | 0.02 | 0.019 | 0.0203 |
Environment configuration
- CPU Model: Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-10870H CPU @ 2.20GHz
- RAM GB: 16
- RAM Model: DDR4
- Speed: 3200 MT/s
- Operating System: Manjaro Linux 21.1.1, Pahvo
- Library Versions:
- Python: 3.9.6
- NumPy: 1.20.3
- Numba: 0.54.0
- Pythran: 0.9.12.post1
- Transonic: 0.4.10
- GCC: 11.1.0
- Note: The benchmarking is performed on the isolated CPU cores for accurate results.
Conclusion
-
NumPy is very efficient, especially for larger datasets. It performs times faster than Python for input size , times faster for a dataset of size, . It gives more than times better performance than Python for input size . The performance of NumPy increases drastically as the number of particles in the datasets increases. Thanks to the vectorized approach in NumPy. Vectorization makes the code look clean and concise to read. That resulted in better performance without any explicit looping, indexing, etc.
-
It uses pre-compiled C code, which adds up to the performance of NumPy. The table shows that the performance of the NumPy is approaching the speed of C++ on increasing the input size. For a dataset of size , NumPy is times slower than C++. For the dataset of size , it reaches equivalent to the speed of C++, with a running time of times, faster than the time taken by C++. NumPy outperforms C++ by times for input size .
How can we accelerate NumPy?
NumPy aims to improve itself and to give better performance for the end-users. It performs well in most cases. But to fill the gaps where NumPy is not so good various compiled methods like Numba, Pythran, etc are used. They play a huge role. Presently, we used Transonic’s JIT Compilation at the backend for NumPy arrays to implement Numba & Pythran. To be specific, we want to compare NumPy’s vectorized approach with the JIT-compiled non-vectorized approach.
- We observed Numba performs times faster than NumPy for input size and times faster for input size . But later, NumPy outperforms Numba by times faster for input size .
- Pythran performs times faster for input size , times better for input size , and times faster than NumPy for input size .
We have compared the performance of NumPy with two of the most popular languages Python and C++, and with popular compiled methods like Numba and Pythran. We distinguished the remarkable change in the behaviour of NumPy as we increment the number of input sizes. NumPy initially performed equivalent to the speed of Python, but, later it changed its behavior from “python-like” nature to “compiled-like” behavior. The running time became similar to accelerators that are to increase the performance of the code. It achieves better performance for scientific computations as well as for solving real-life situations. That’s NumPy. It stands explicitly well in all kinds of circumstances.